#Competition for startup funding
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
From Vision to Reality: How to Scale Your Business in a Competitive Market
Introduction Scaling a business in today’s competitive market is not just a dream; it’s a necessity for longevity and success. Every entrepreneur starts with a vision, but transforming that vision into a tangible reality requires strategic planning, resilience, and innovative approaches. In this article, we will explore effective strategies for scaling your business, discussing key aspects such…
#best practices for brand management#Branding strategies for small businesses#building brand loyalty#Business#business growth strategies#Competitive#corporate social responsibility#creating a strong brand identity#customer relationship management#digital marketing for startups#e-commerce tips for businesses#how to scale your business.#how to start a successful business#importance of social media for businesses#influencer marketing for brands#Market#Reality#Scale#small business funding options#top business trends 2024#Vision
0 notes
Text
How Market Research Strengthens Your Investor Pitch | Capmaven

Investors need more than a compelling story—they want data-driven confidence. Market research helps startups define their target audience, conduct competitor analysis, and build scalable revenue models. Get industry-specific insights with Capmaven. Let’s connect today at Capmaven.co
#Market Research#Investor Pitch#Startup Strategy#Business Growth#Financial Modeling#Competitive Analysis#Target Market#Startup Funding#Entrepreneurship
0 notes
Text
🎖️🌎 Out of hundreds of companies, Make My Day has been selected as a finalist for The 7th China (Shenzhen) Innovation and Entrepreneurship International Competition (Israeli Division) Finals! This is the biggest and most exclusive international innovation competition coming out of #China!

Taking part in this international competition is an honor for us as an #Energy and #Environment startup with #Climatech#technology that can revolutionize the automobile industry.
The #Shenzhen Innovation & Entrepreneurship International Competition celebrates innovation, entrepreneurship, and global collaboration, and is a gateway to a thriving ecosystem of innovation, collaboration, and global partnerships. For more information, visit the competition's official website: https://lnkd.in/dWQK3gNT
China (Shenzhen) Innovation and Entrepreneurship International CompetitionOhad MaromNisan KatzCnaan AvivLee paztal
#entrepreneurship#China#innovation#prize#event#Shenzhen#competition#startup#shenzhen#china#ShenzhenInnovationCompetition#InnovationEcosystem#GlobalInnovation#StartupJourney#tech#collaboration#funding#MakeMyDay#InternationalCompetition#Entrepreneurship#EV#Energy#Climatech
0 notes
Video
youtube
Should Billionaires Exist?
Do billionaires have a right to exist?
America has driven more than 650 species to extinction. And it should do the same to billionaires.
Why? Because there are only five ways to become one, and they’re all bad for free-market capitalism:
1. Exploit a Monopoly.
Jamie Dimon is worth $2 billion today… but not because he succeeded in the “free market.” In 2008, the government bailed out his bank JPMorgan and other giant Wall Street banks, keeping them off the endangered species list.
This government “insurance policy” scored these struggling Mom-and-Pop megabanks an estimated $34 billion a year.
But doesn’t entrepreneur Jeff Bezos deserve his billions for building Amazon?
No, because he also built a monopoly that’s been charged by the federal government and 17 states for inflating prices, overcharging sellers, and stifling competition like a predator in the wild.
With better anti-monopoly enforcement, Bezos would be worth closer to his fair-market value.
2. Exploit Inside Information
Steven A. Cohen, worth roughly $20 billion headed a hedge fund charged by the Justice Department with insider trading “on a scale without known precedent.” Another innovator!
Taming insider trading would level the investing field between the C Suite and Main Street.
3. Buy Off Politicians
That’s a great way to become a billionaire! The Koch family and Koch Industries saved roughly $1 billion a year from the Trump tax cut they and allies spent $20 million lobbying for. What a return on investment!
If we had tougher lobbying laws, political corruption would go extinct.
4. Defraud Investors
Adam Neumann conned investors out of hundreds of millions for WeWork, an office-sharing startup. WeWork didn’t make a nickel of profit, but Neumann still funded his extravagant lifestyle, including a $60 million private jet. Not exactly “sharing.”
Elizabeth Holmes was convicted of fraud for her blood-testing company, Theranos. So was Sam Bankman-Fried of crypto-exchange FTX. Remember a supposed billionaire named Donald Trump? He was also found to have committed fraud.
Presumably, if we had tougher anti-fraud laws, more would be caught and there’d be fewer billionaires to preserve.
5. Get Money From Rich Relatives
About 60 percent of all wealth in America today is inherited.
That’s because loopholes in U.S. tax law —lobbied for by the wealthy — allow rich families to avoid taxes on assets they inherit. And the estate tax has been so defanged that fewer than 0.2 percent of estates have paid it in recent years.
Tax reform would disrupt the circle of life for the rich, stopping them from automatically becoming billionaires at their birth, or someone else’s death.
Now, don’t get me wrong. I’m not arguing against big rewards for entrepreneurs and inventors. But do today’s entrepreneurs really need billions of dollars? Couldn’t they survive on a measly hundred million?
Because they’re now using those billions to erode American institutions. They spent fortunes bringing Supreme Court justices with them into the wild.They treated news organizations and social media platforms like prey, and they turned their relationships with politicians into patronage troughs.
This has created an America where fewer than ever can become millionaires (or even thousandaires) through hard work and actual innovation.
If capitalism were working properly, billionaires would have gone the way of the dodo.
434 notes
·
View notes
Text
No, “convenience” isn’t the problem
I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in CHICAGO (Apr 17), Torino (Apr 21) Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

Using Amazon, or Twitter, or Facebook, or Google, or Doordash, or Uber doesn't make you lazy. Platform capitalism isn't enshittifying because you made the wrong shopping choices.
Remember, the reason these corporations were able to capture such substantial market-share is that the capital markets saw them as a bet that they could lose money for years, drive out competition, capture their markets, and then raise prices and abuse their workers and suppliers without fear of reprisal. Investors were chasing monopoly power, that is, companies that are too big to fail, too big to jail, and too big to care:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/04/teach-me-how-to-shruggie/#kagi
The tactics that let a few startups into Big Tech are illegal under existing antitrust laws. It's illegal for large corporations to buy up smaller ones before they can grow to challenge their dominance. It's illegal for dominant companies to merge with each other. "Predatory pricing" (selling goods or services below cost to prevent competitors from entering the market, or to drive out existing competitors) is also illegal. It's illegal for a big business to use its power to bargain for preferential discounts from its suppliers. Large companies aren't allowed to collude to fix prices or payments.
But under successive administrations, from Jimmy Carter through to Donald Trump, corporations routinely broke these laws. They explicitly and implicitly colluded to keep those laws from being enforced, driving smaller businesses into the ground. Now, sociopaths are just as capable of starting small companies as they are of running monopolies, but that one store that's run by a colossal asshole isn't the threat to your wellbeing that, say, Walmart or Amazon is.
All of this took place against a backdrop of stagnating wages and skyrocketing housing, health, and education costs. In other words, even as the cost of operating a small business was going up (when Amazon gets a preferential discount from a key supplier, that supplier needs to make up the difference by gouging smaller, weaker retailers), Americans' disposable income was falling.
So long as the capital markets were willing to continue funding loss-making future monopolists, your neighbors were going to make the choice to shop "the wrong way." As small, local businesses lost those customers, the costs they had to charge to make up the difference would go up, making it harder and harder for you to afford to shop "the right way."
In other words: by allowing corporations to flout antimonopoly laws, we set the stage for monopolies. The fault lay with regulators and the corporate leaders and finance barons who captured them – not with "consumers" who made the wrong choices. What's more, as the biggest businesses' monopoly power grew, your ability to choose grew ever narrower: once every mom-and-pop restaurant in your area fires their delivery drivers and switches to Doordash, your choice to order delivery from a place that payrolls its drivers goes away.
Monopolists don't just have the advantage of nearly unlimited access to the capital markets – they also enjoy the easy coordination that comes from participating in a cartel. It's easy for five giant corporations to form conspiracies because five CEOs can fit around a single table, which means that some day, they will:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/18/cursed-are-the-sausagemakers/#how-the-parties-get-to-yes
By contrast, "consumers" are atomized – there are millions of us, we don't know each other, and we struggle to agree on a course of action and stick to it. For "consumers" to make a difference, we have to form institutions, like co-ops or buying clubs, or embark on coordinated campaigns, like boycotts. Both of these tactics have their place, but they are weak when compared to monopoly power.
Luckily, we're not just "consumers." We're also citizens who can exercise political power. That's hard work – but so is organizing a co-op or a boycott. The difference is, when we dog enforcers who wield the power of the state, and line up behind them when they start to do their jobs, we can make deep structural differences that go far beyond anything we can make happen as consumers:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/18/administrative-competence/#i-know-stuff
We're not just "consumers" or "citizens" – we're also workers, and when workers come together in unions, they, too, can concentrate the diffuse, atomized power of the individual into a single, powerful entity that can hold the forces of capital in check:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/10/an-injury-to-one/#is-an-injury-to-all
And all of these things work together; when regulators do their jobs, they protect workers who are unionizing:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/06/goons-ginks-and-company-finks/#if-blood-be-the-price-of-your-cursed-wealth
And strong labor power can force cartels to abandon their plans to rig the market so that every consumer choice makes them more powerful:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/01/how-the-writers-guild-sunk-ais-ship/
And when consumers can choose better, local, more ethical businesses at competitive rates, those choices can make a difference:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/07/10/view-a-sku/
Antimonopoly policy is the foundation for all forms of people-power. The very instant corporations become too big to fail, jail or care is the instant that "voting with your wallet" becomes a waste of time.
Sure, choose that small local grocery, but everything on their shelves is going to come from the consumer packaged-goods duopoly of Procter and Gamble and Unilever. Sure, hunt down that local brand of potato chips that you love instead of P&G or Unilever's brand, but if they become successful, either P&G or Unilever will buy them out, and issue a press release trumpeting the purchase, saying "We bought out this beloved independent brand and added it to our portfolio because we know that consumers value choice."
If you're going to devote yourself to solving the collective action problem to make people-power work against corporations, spend your precious time wisely. As Zephyr Teachout writes in Break 'Em Up, don't miss the protest march outside the Amazon warehouse because you spent two hours driving around looking for an independent stationery so you could buy the markers and cardboard to make your anti-Amazon sign without shopping on Amazon:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/07/29/break-em-up/#break-em-up
When blame corporate power on "laziness," we buy into the corporations' own story about how they came to dominate our lives: we just prefer them. This is how Google explains away its 90% market-share in search: we just chose Google. But we didn't, not really – Google spends tens of billions of dollars every single year buying up the search-box on every website, phone, and operating system:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/21/im-feeling-unlucky/#not-up-to-the-task
Blaming "laziness" for corporate dominance also buys into the monopolists' claim that the only way to have convenient, easy-to-use services is to cede power to them. Facebook claims it's literally impossible for you to carry on social relations with the people that matter to you without also letting them spy on you. When we criticize people for wanting to hang out online with the people they love, we send the message that they need to choose loneliness and isolation, or they will be complicit in monopoly.
The problem with Google isn't that it lets you find things. The problem with Facebook isn't that it lets you talk to your friends. The problem with Uber isn't that it gets you from one place to another without having to stand on a corner waving your arm in the air. The problem with Amazon isn't that it makes it easy to locate a wide variety of products. We should stop telling people that they're wrong to want these things, because a) these things are good; and b) these things can be separated from the monopoly power of these corporate bullies:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/08/divisibility/#technognosticism
Remember the Napster Wars? The music labels had screwed over musicians and fans. 80 percent of all recorded music wasn't offered for sale, and the labels cooked the books to make it effectively impossible for musicians to earn out their advances. Napster didn't solve all of that (though they did offer $15/user/month to the labels for a license to their catalogs), but there were many ways in which it was vastly superior to the system it replaced.
The record labels responded by suing tens of thousands of people, mostly kids, but also dead people and babies and lots of other people. They demanded an end to online anonymity and a system of universal surveillance. They wanted every online space to algorithmically monitor everything a user posted and delete anything that might be a copyright infringement.
These were the problems with the music cartel: they suppressed the availability of music, screwed over musicians, carried on a campaign of indiscriminate legal terror, and lobbied effectively for a system of ubiquitous, far-reaching digital surveillance and control:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/02/nonbinary-families/#red-envelopes
You know what wasn't a problem with the record labels? The music. The music was fine. Great, even.
But some of the people who were outraged with the labels' outrageous actions decided the problem was the music. Their answer wasn't to merely demand better copyright laws or fairer treatment for musicians, but to demand that music fans stop listening to music from the labels. Somehow, they thought they could build a popular movement that you could only join by swearing off popular music.
That didn't work. It can't work. A popular movement that you can only join by boycotting popular music will always be unpopular. It's bad tactics.
When we blame "laziness" for tech monopolies, we send the message that our friends have to choose between life's joys and comforts, and a fair economic system that doesn't corrupt our politics, screw over workers, and destroy small, local businesses. This isn't true. It's a lie that monopolists tell to justify their abuse. When we repeat it, we do monopolists' work for them – and we chase away the people we need to recruit for the meaningful struggles to build worker power and political power.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/12/give-me-convenience/#or-give-me-death

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
351 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Invest Based on the Planet in your 2ND House:
1. Sun in 2nd House – Invest in personal branding, leadership roles, gold, creative ventures, luxury goods, or high-status assets.
2. Moon in 2nd House – Invest in real estate, food industry, family businesses, emotional-driven markets, fluctuating assets, or savings for security.
3. Mercury in 2nd House – Invest in communication, tech, education, writing, trading, intellectual property, or diverse, fast-moving markets.
4. Venus in 2nd House – Invest in art, fashion, beauty industry, luxury goods, relationships, passive income, or aesthetically valuable assets.
5. Mars in 2nd House – Invest aggressively in business, startups, physical assets, high-risk ventures, action-driven markets, or competitive industries.
6. Jupiter in 2nd House – Invest in education, travel, international markets, publishing, philanthropy, expansive assets, or lucky long-term ventures.
7. Saturn in 2nd House – Invest conservatively in long-term assets, retirement funds, real estate, stable businesses, disciplined savings, or structured investments.
8. Uranus in 2nd House – Invest in tech, unconventional markets, cryptocurrency, innovative startups, sudden opportunities, or futuristic industries.
9. Neptune in 2nd House – Invest in creative fields, spirituality, film, music, intangible assets, philanthropy, or passive income sources.
10. Pluto in 2nd House – Invest in transformative industries, power-driven markets, hidden assets, real estate, wealth management, or high-stakes opportunities.
#astrology#astronomy#numerology#spirituality#twin flames#spiritual awakening#spiritual growth#spiritual healing#spiritual journey#intrusive thoughts#Neptune#Jupiter#the sun#sun#Uranus#mars#Venus#Pluto
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
I took a huge break from tech and the internet. Recently, I rejoined the tech world for a contract gig and decided to peek at Twitter X again... and omg. I feel like I just walked into the weirdest reality show.
Everyone’s hustling 24/7 for their startup, and it feels like anyone can think of a half-baked idea, get VC funding, go viral on X, and then somehow make even more money. AND not because their product actually works, but because of the hype around it.
And honestly? I feel disillusioned.
I’m tired of:
The glorification of hustle
The extraction of labor to benefit shareholders
Building things that don’t actually make the world better
For a while I began to think I hate tech. But it’s not that. I hate what late-stage capitalism has done to it.
Is it asking for to much to find work that includes:
Rest and boundaries
Work with real, tangible meaning
Collaboration without competition
Wholesomeness and authenticity over manipulation
????
Am I missing something here? Why do we do this? I think I will leave X again but I will try out bluesky and see how the vibes are over there...
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
TYPE § drabble
PLOT ; Ellie and Abby, rival hockey captains from wealthy families, clash fiercely on ice, their legacies and attraction fueling intense competition.
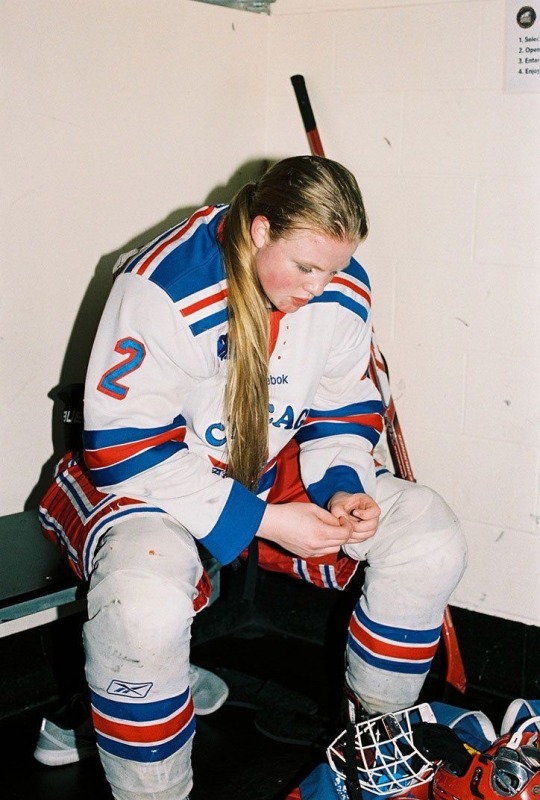




The rink smelled like frost and fury, a sharp tang of shaved ice mingling with the sweat-soaked leather of hockey gear. Ellie Williams leaned against the boards, her stick balanced across her shoulders like a yoke, her breath fogging in the cold air of the Seattle Storm’s home arena.
Her green eyes, narrowed beneath the shadow of her visor, tracked the opposing team’s captain across the ice. Abby Anderson, all long limbs and golden braid, glided through warm-ups with a grace that belied the brute force she unleashed in games. Ellie’s jaw tightened. Tonight’s match wasn’t just another game in the Women’s Pacific Hockey League—it was personal.
Ellie’s family name carried weight in Seattle. The Williams legacy was etched into the city’s skyline: real estate empires, tech startups, and a foundation that funded half the youth hockey programs in the state. Her father, Joel, was the anomaly—a self-made man who’d clawed his way from a Texas trailer park to boardrooms, building his fortune with nothing but grit and a knack for reading people.
He’d raised Ellie to be tough, to carve her own path, even if it meant skating through a world that expected her to trade her stick for a suit. She’d chosen the ice instead, her cropped auburn hair slicked back, her jersey hanging loose over broad shoulders honed by years of training. Ellie was all edges—sharp elbows, sharper tongue ( one she used well ), and a playing style that was equal parts precision and chaos.
Across the rink, Abby Anderson was a different kind of force. The Andersons were old money, their name synonymous with philanthropy and power. Her father, Dr. Jerry Anderson, was a renowned surgeon whose foundation bankrolled medical clinics across the Northwest. Abby grew up in a world of galas and expectations, her childhood split between private tutors and figure skating lessons. But she’d traded sequins for skates, choosing hockey over her mother’s dreams of a debutante daughter. Now, in her feminine era, Abby leaned into her softness off the ice—flowing blonde hair, delicate gold jewelry, and a wardrobe of tailored athleisure that screamed understated wealth. On the ice, though, she was a titan, her six-foot frame a wall of muscle and menace, her stick an extension of her will.
The rivalry between Ellie and Abby wasn’t just about hockey. It was about legacy, about two women from gilded cages proving they were more than their last names. They’d clashed since their junior league days, their games a brutal ballet of checks and goals. Ellie’s agility and trash-talking swagger grated on Abby’s disciplined intensity; Abby’s relentless physicality and cool-headed taunts drove Ellie to the brink. Their last meeting had ended with Ellie in the penalty box, blood trickling from a split lip, and Abby smirking from the bench. Tonight, with the Storm facing Abby’s Portland Sirens for a playoff spot, the stakes were higher than ever.
Ellie adjusted her gloves, the leather creaking as she flexed her fingers. Joel was in the stands, his weathered face a quiet anchor amid the roaring crowd. He’d never pushed her into hockey, but he’d been there for every 5 a.m. practice, every bruised ego, every triumph. “You don’t owe nobody nothin’,” he’d told her once, his drawl thick after a long day. “But if you’re gonna fight, fight like hell.” Ellie intended to.
On the other side, Abby’s gaze flicked to the luxury box where her parents sat. Her father’s approval was a rare currency, doled out in measured nods. Her mother, elegant in a cashmere coat, had softened toward Abby’s career but still flinched at every hit her daughter took. Abby had learned early to compartmentalize—to be the poised daughter at fundraisers and the unrelenting captain on the ice. But Ellie Williams had a way of cracking her composure, those green eyes sparking with a challenge Abby couldn’t ignore.
The whistle blew, and the teams lined up for the face-off. Ellie crouched at center, her stick tapping the ice, her smirk a silent dare. Abby mirrored her, her blue eyes locked on Ellie’s, her braid swinging as she leaned in. The puck dropped, and the world narrowed to the scrape of blades and the crack of sticks. Ellie won the face-off, snapping the puck to her winger, but Abby was already on her, shoulder slamming into Ellie’s chest with a force that rattled her teeth. Ellie stumbled, recovered, and chased the play, her legs pumping, her mind a blur of strategy and spite.
The first period was a war. Ellie danced through defenders, her wrist shot pinging off the crossbar. Abby answered with a bone-crushing check that sent a Storm player sprawling, her team capitalizing with a goal. The crowd roared, a sea of green and blue clashing with Portland’s red. Ellie’s trash talk flowed—“That all you got, Anderson?”—and Abby’s retorts were icy: “Keep barking, Williams. I’ll shut you up soon enough.” Their teammates exchanged glances, knowing better than to get between the two captains when they were like this.
Off the ice, their lives intersected in ways neither acknowledged. They’d crossed paths at charity events, their families’ foundations often collaborating. Ellie, in a rare suit, had once caught Abby’s eye across a ballroom, her blonde hair loose, her laugh unguarded. Abby, in turn, had seen Ellie at a youth clinic, patiently teaching kids to skate, her usual scowl replaced by a rare softness. Those moments lingered, unspoken, buried under the weight of their rivalry.
By the second period, the score was tied, and the tension was a living thing. Ellie scored on a breakaway, her shot a laser past the Sirens’ goalie, and she celebrated with a spin, pointing at Abby with her stick. Abby’s jaw clenched, and minutes later, she answered with a slapshot that left the net vibrating. The third period loomed, and both knew it would come down to the wire.
In the locker room, Ellie’s coach barked strategy, but her mind was on Abby.
“I’ll shut you up soon enough.” Constantly repeating.
She hated how the blonde filled her thoughts, how every hit felt like a conversation, every goal a confession. Abby, meanwhile, sat in the Sirens’ locker room, re-taping her stick, her calm exterior hiding a flicker of unease. Ellie’s defiance sparked something in her—a hunger to win, to dominate, but also a pull she didn’t understand.
As the final period began, the ice was theirs. Ellie and Abby traded blows, their families’ legacies, their unspoken truths etched into every move. With seconds left and the score tied, Ellie stole the puck, and barreled toward the net. Abby was there, her last stand a desperate lunge. Their sticks clashed, their bodies collided, and the puck skittered free. The buzzer sounded, and the game ended in a draw—but for Ellie and Abby, it was far from over.
Their rivalry was a fire, a spark that burned brighter in the cold, and as they skated off, their gazes locked, both knew this was only the beginning.
Should I continue this?
Love Tana
#ellabs#ellie williams#abby the last of us#abby anderson#abby tlou#ellie the last of us#joel and ellie#ellie tlou#ellie willams x reader#ellie x abby#the last of us#tlou smau#tlou drabble#drabble#hockeyau#tanawritesdrabbles£
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
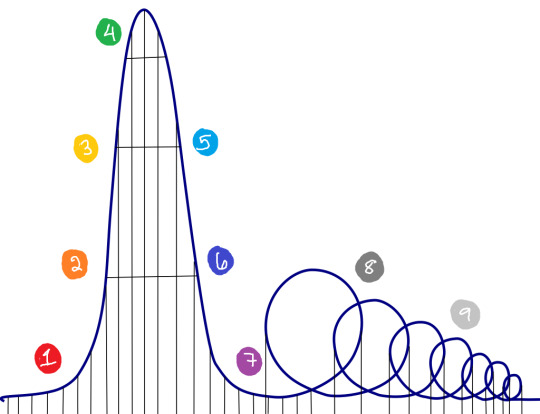
this is the startup coaster as I'm familiar with it:
(1) three guys named scott snag a few million in seed funding, hire a few engineers to work with them in the abandoned wework they're renting from the ghost of a 15th century land baron.
(2) headcount slowly grows, they release a product that "works" but it's either cheap as hell or free so people are starting to adopt it; adoption is a sign of growth, which in turn yields more funding from eager investors.
(3) scott^3 have enough cash reserves to move into a real office and hire marketing/sales people, product improves a bit. still not even close to being profitable but it's okay because funding continues to pour in!
(4) incremental product improvements, user adoption crescendoes, maybe another funding round. possible hiring frenzy to follow. cue a chorus of scotts, in perfect unison: "our company is valued at almost at a billion dollars! an IPO is just around the corner!"
(5) investor money becomes harder and harder to come by over time; company slows spending.
(6) "well, all we have to do is focus on revenue instead of growth... profitability is within reach." management may or may not make poor decisions that spur original critical employees to jump ship, taking their expertise and guiding philosophy with them.
(7) money continues to hemorrhage with no VC infusions in sight. company makes significant cuts to their workforce, pares back their roadmap.
(8) in the absence of key personnel (and without the necessary cushion to develop new features or offer competitive pricing), the product either stagnates or gets noticeably worse. users revolt and either threaten to leave or actually do.
(9) final death spiral where revenue continues to dry up, which leads to more layoffs, which makes the product worse, which means users continue to churn, which makes revenue dry up even more. any investors cut their losses and move on to their next prospect. scott, scott, and scott either go on the podcast circuit or start over again to get seed funding for a new startup that they can only describe as "the uber of canine saunas"
348 notes
·
View notes
Text
President Donald Trump’s sweeping tariffs on Chinese imports have sent millions of manufacturers, retailers, and small businesses on both sides of the Pacific scrambling to cope with a sudden and punishing rise in costs. After Beijing responded with its own retaliatory measures, the White House said that a wide range of Chinese-made goods—from toys to electronics—will now face an effective tariff rate of 145 percent, a steep jump from the 34 percent figure Trump initially outlined just last week.
But despite looming economic pain, China is not backing down or making concessions to Trump. If anything, the government appears more defiant than ever, especially after some political narratives about the country’s manufacturing strength have started to shift in recent years. In the long run, in fact, an escalating battle with the US could wind up being an opportunity for China to leverage its growing soft power. “If the US is determined to fight a tariff and trade war, China’s response will continue to the end,” Liu Pengyu, spokesperson for the Chinese embassy in Washington, DC, said in a statement to WIRED.
The US previously justified its punitive trade measures against China by citing the country’s troubling human rights record and accusing it of repeatedly stealing American intellectual property. But China has now developed its own global tech brands, is home to a leading artificial intelligence startup, and has opened more branches of domestic drink shop Mixue than there are Starbucks or McDonald's locations worldwide. The Trump administration’s alleged human rights abuses, meanwhile, are alarming civil liberties groups and observers around the world.
“This is kind of an interesting confluence of events where you have this soft power win over on the China side combined with effectively a complete abdication of soft power altogether from the United States,” says Kevin Xu, founder of the technology hedge fund Interconnected Capital and a former White House staffer under President Obama.
Many Chinese citizens seem pleased that their leaders are standing up to the US, though public polling in the country can be sparse and unreliable. As Trump’s tariffs went into effect, the Chinese government appeared to censor hashtags that mentioned the specifics of the measures, like “104 tariff rate,” but it allowed others focused on making fun of the United States to continue circulating. “America is fighting a trade war while begging for eggs,” read one particularly popular hashtag coined by China’s state broadcaster.
“We support our country in standing firm to the end! We’re not afraid of temporary hardship—what we fear is eternal cowardice," says the owner of an artificial Christmas tree factory in China who asked to remain anonymous due to the risks of speaking to foreign media outlets. The owner tells WIRED that the tariffs are already having negative impacts on her industry, and she expects the competition for non-US markets like South America and Russia to be stiff next year, but “no matter what, we'll get through it.”
Trump administration officials have promoted the tariffs as a way to boost US manufacturing and create more high-paying jobs. But American small business owners painted a very different picture of the situation on TikTok. In one video, the founder of a trendy hair accessories brand rolled her eyes and explained that the company’s products “literally cannot be made here.” In another, the CEO of a shoe company similarly said China “is just the only place I could manufacture.” The owner of a company that makes self-checkout kiosks lamented about how awful his experiences have been working with suppliers in the US compared to those in China. “What it’s about is Americans are a bunch of babies and they are hard to work with,” he told the camera.
The founder of a London-based clothing brand struck a more heartwarming tone, uploading a slideshow of pictures of herself posing with the garment workers her company partners with in China, set to The Fray song “Look After You.” The text overlaid on one photo read “Our wins are their wins.” The TikTok post received over 55,000 likes, an indication of how attitudes toward China have evolved among at least some Western consumers, compared to the past, when the country’s factories were mostly associated with pumping out cheap, flimsy goods. “Suddenly people see, oh, it’s not this imagined ‘slave labor’ that's making my clothes, they're actually humans,” says Tianyu Fang, a fellow at the New America think tank and one of the cofounders of the Chinese internet culture newsletter Chaoyang Trap.
In recent weeks, as the Trump administration’s ever-changing trade policies enraged close American allies like Canada, a number of prominent commentators have even begun suggesting that perhaps the era of American exceptionalism was over. The coming decades, they argued, would now be defined by the rise of China.
“The Chinese century, brought to you by Donald Trump,” David Frum, a staff writer at The Atlantic and former speechwriter for George W. Bush said in a social media post on April 2. New York Times opinion writer Thomas Friedman published a column the same day raving about a recent trip to China during which he witnessed the country’s impressive infrastructure and technological development. It was headlined “I Just Saw the Future. It Was Not in America.”
“When people say this is the Chinese century, what they really mean is that the consensus that this will be the American century is being broken,” says Fang.
Growing Influence
When Trump’s most comprehensive tariffs caused global stock markets to take a nosedive earlier this week, US social media influencer Darren Watkins Jr., better known as IShowSpeed to his over 100 million collective followers, was wrapping up a sprawling tour across China with stops in Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, and other cities. Watkins spent days livestreaming himself mingling with Chinese celebrities and taking a boat ride with Hong Kong’s glittering skyline as the backdrop. By broadcasting in real time, IShowSpeed’s fans got an “unprecedented opportunity” to see “an unfiltered China,” Yaling Jiang, CEO of the strategy firm ApertureChina, wrote in her newsletter.
Many Americans got another direct glimpse inside China earlier this year when the US was set to ban TikTok nationwide. Anticipating the app might soon disappear, hundreds of thousands of people flocked to RedNote, another Chinese-owned social media app, where they saw posts of people in China showing off their domestic-made electric cars and comfortable urban apartments. TikTok itself, which was created by the Chinese tech giant ByteDance, is a testament to China’s growing soft power. Trump has vowed to save the app, and despite warnings from US lawmakers about the data security risks it poses, fewer Americans support banning it than did a few years ago.
But positive depictions of China won’t shield it from the economic damage ahead. Trump’s tariffs are so high that they will likely bring trade between the world’s two largest economies to a screeching halt. The signs of that disruption are already visible: Bloomberg reported that Amazon has canceled a number of wholesale product orders, like $500,000 worth of Chinese-made beach chairs for the upcoming US summer season, while a toy maker in China’s Guangdong province told The Wall Street Journal that a longtime client in Maryland similarly canceled a shipment scheduled to be delivered in June.
In as little as a few weeks, Americans may have a harder time finding some products on store shelves, which will eventually lead to higher consumer prices. The Chinese workers who make those items, meanwhile, could soon find themselves out of work. “The US is facing shortages and inflation, and on the Chinese side, they’re facing job losses and deflation,” says Gerard DiPippo, acting associate director of the RAND China Research Center and an expert on China’s economy. DiPippo adds that he’s stocking up on cooking ingredients from China in case they become unavailable, like szechuan peppercorns.
While there are some ways the Chinese government could try to stimulate spending and prop up local businesses, its options are fairly limited. Over the past few years, a domestic housing market crash has eroded the savings of China’s middle class and youth unemployment has soared, causing demand for things like shopping and eating at restaurants to fall. In response, China focused even more on increasing exports, making the country especially vulnerable to Trump’s attacks. China sent about $400 billion worth of goods to the US last year, and there are few other places it could shift that trade instead.
It’s unclear how things will unfold. China’s economic challenges could limit its ability to extend influence globally, and many will continue to view its authoritarian regime with skepticism. In the future, the cultural void left by the US may remain vacant as the world becomes increasingly fragmented. “I personally see the vacuum scenario more possible, where we’re all kind of fending for ourselves,” says Xu.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crafting Your E-Commerce Strategy: Key Tips for Competitive Advantage
In today’s digital age, crafting an effective e-commerce strategy is essential for businesses looking to gain a competitive advantage. With numerous brands vying for attention online, a well-defined e-commerce strategy not only promotes sales but also helps in building brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. This comprehensive guide will walk you through essential tips and techniques to refine…
#Advantage#best practices for brand management#Branding strategies for small businesses#building brand loyalty#business growth strategies#Competitive#corporate social responsibility#Crafting#creating a strong brand identity#customer relationship management#digital marketing for startups#e-commerce tips for businesses#ECommerce#how to scale your business.#how to start a successful business#importance of social media for businesses#influencer marketing for brands#Key#small business funding options#Strategy#Tips#top business trends 2024
0 notes
Text

Why Do We Have to "Campaign" to Deserve Help?
Wildfires in California have become a grim ritual. Every season, hundreds of homes go up in flames, entire neighborhoods are destroyed, and thousands of people are forced to rebuild their lives.
But beyond the flames, another harsh reality emerges: not all victims are equal in the face of disaster.
A recent article by Jonas Valdez in The Intercept highlighted a disturbing bias: after the Eaton fire, which devastated the city of Altadena, GoFundMe campaigns overwhelmingly favored wealthier white families, while Black and working-class residents were left behind.
Why this inequality? Because on GoFundMe, mutual aid works like a market. Those who know how to sell themselves, tell a compelling story, and mobilize their networks receive more donations. The rest remain in the shadows.
Should people really need to be good communicators to deserve help after a disaster?
Why must victims beg, campaign, and win over an audience, when aid should be automatic?
We have entered an era where solidarity is privatized. It is no longer a right but a service, governed by the laws of marketing and social capital.
And what if the real problem goes beyond GoFundMe?
Social Aid Has Become a Competition
Altadena is not an isolated case. The Intercept article cites several studies that reveal a systemic bias in online fundraising:
Middle-class and working-class people receive fewer donations than wealthier families.
Campaigns led by Black or Hispanic individuals are less successful than those led by white people.
Older, isolated victims, or those less skilled with the internet, struggle to raise funds.
In other words: GoFundMe does not reflect the urgency of needs—it reflects communication skills.
Imagine two victims of the same fire:
One has influential friends, a great photo, a moving text, and a powerful video. They raise $50,000 in a week.
The other, older, isolated, and uncomfortable with online tools, barely collects $800.
The problem is not a lack of generosity. The problem is that generosity follows invisible biases—shaped by social networks, class dynamics, and the mechanisms of emotional capitalism.
A False Illusion of Solidarity: GoFundMe Is Not an Alternative, It’s a Symptom
The Intercept article highlights a bias in crowdfunding, but its critique remains internal—it points out the unfairness of campaigns without questioning why aid relies on this model in the first place.
In reality, the issue goes beyond GoFundMe: we have replaced a system of collective aid with individual competition.
Before, when disaster struck, governments and institutions provided automatic assistance to victims.
Today, each person is pushed to fend for themselves—to "pitch" their distress like a startup project.
This shift is profound: mutual aid is no longer a guaranteed social right, but a marketplace where everyone must compete to be seen.
If you're a good communicator, you get help.
If you're invisible, you don’t exist.
The injustice of GoFundMe is not a flaw—it’s a feature of the system.
GoFundMe: A Social Lottery Disguised as Charity?
If this trend continues, it won’t be surprising to see in the future:
Students launching GoFundMe campaigns to pay for their education.
Patients raising money for medical treatment.
Disaster victims competing for public attention.
This is a slippery slope, where all forms of aid become commodities subject to market forces.
Philosopher John Rawls argued that in a just society, aid should go first to the most vulnerable. But here, we see the opposite: those who need help the most are the ones who receive the least.
So, the choice is clear:
A world where aid depends on storytelling and social capital → Competition, inequality, and social Darwinism applied to charity.
A world where aid is a structured and universal right → Social justice, equitable redistribution, and collective mechanisms.
Today, we are dangerously moving toward the first model.
What Kind of Society Do We Want?
The Intercept article exposes an immediate injustice, but it doesn’t ask the fundamental question:
Why do we accept that a private platform decides who gets to survive?
Why is aid treated as a market rather than a fundamental right?
If we continue on this path, we will soon live in a society where everyone must beg for their own survival.
Yet, this is not inevitable. We still have time to reject this shift.
So, do we want a society where mutual aid is a lottery? Or a world where no one has to beg to exist?
For a deeper analysis, read my full article on Medium: https://medium.com/@ptit.tolier/do-we-have-to-beg-to-survive-bfd4f9324d89
Thank you for reading.
P’tit Tôlier
"Essayist & popularizer. I analyze the world through accessible philosophical essays. Complex ideas, explained simply—to help us reflect on our times."

#crowdfunding#philosophy#social justice#SocietyAndEthics#HumanRights#mutual aid#charity#EmotionalCapitalism#PrivatizedAid#GoFundMeAnalysis#FundraisingBias#SurvivalEconomy#WealthInequality#Neoliberalism#OnlineFundraising#DigitalSurvival#FinancialInequality#HelpOrMarketing#TheEthicsOfAid#WhoDeservesHelp#SocialMediaInfluence#CharityOrBusiness#ViralGenerosity#MarketingForSurvival
5 notes
·
View notes
Text










2025 Homevalley Global Entrepreneurs Competition
Registration Now Open
March 1, 2025 — The highly anticipated 2025 Homevalley Global Entrepreneurs Competition officially launched today, with global registration now open. Innovators and entrepreneurs worldwide are invited to participate, with registration available until May 10. This competition aims to build a global entrepreneurial ecosystem, offering a dedicated investment fund of RMB 300 million to recruit high-quality projects and accelerate technological innovation and industrial upgrades in Shanghai.
Key Highlights of the Competition
Expanded Global Reach
Five major competition zones across 18 Cities/Countries: Including North America (West/ East), Europe, Asia, and Oceania.
Six Competition Tracks
New track: Advanced Equipment Manufacturing, joining Artificial Intelligence & Software Technology, Electronic Information Technology, Life Sciences & Health, Green Environmental Protection, and Cultural Innovation/New Consumer Trends.
Generous Awards & Funding
150 award slots across all stages, supported by a RMB 300 million investment fund.
Individual project funding ranges from RMB 3 million to RMB 10 million.
Post-Competition Benefits - Shanghai Incubation Program
Finalists gain access to a 1-6 month fully funded incubation program in Shanghai, covering flights, accommodation, workspace, and mentorship.
Policy support via integrated municipal and district-level resources.
Global Talent Scout Incentives
"Global Talent Scout Award" : Up to RMB 500,000 for individuals/organizations recommending outstanding projects.
Prize Structure
Regional Preliminary & Semi-Final Rounds:
Preliminary Awards:
First Prize: $1,000
Second Prize: $500
Third Prize: $300
Semi-Final Awards:
First Prize: $5,000
Second Prize: $3,000
Third Prize: $1,000
Special prizes include Amazon Web Services credits (up to $25,000).
Global Finals:
Gold Award: RMB 100,000
Silver Award: RMB 50,000
Bronze Award: RMB 30,000
Project Implementation Support
Funding: RMB 3–10 million for outstanding projects.
Talent Subsidies: Up to RMB 2 million based on qualifications and location.
Office Space: Free workspace up to 300 sqm in Shanghai.
Residency Support: Shanghai residency quotas for up to 5 core team members.
Credit Financing: Loans up to RMB 30 million.
Competition Timeline
Registration: March 1 – May 10, 2025
Regional Preliminary Rounds: May 11–31, 2025
Global Semi-Finals: June 2025
Global Finals: August 2025
Eligibility
Open to global innovators who are founders or largest shareholders of submitted projects, regardless of nationality.
Organizers & Partners
Hosted by Homevalley, with support from 100+ investors, angel networks, and media partners. The competition bridges startups with Shanghai and Yangtze River Delta industrial resources.
How to Apply
Scan the QR code below or visit the official website:
www.homevalley.net (Home)
www.homevalleycapital.com (Abroad)
For details, follow the official WeChat account **"归心谷"** or email [email protected].
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Global Recognition Can Accelerate Brand Growth and Credibility

You’re building a brand, and you want it to stand out. In 2025, competition is fierce — customers have endless options, and trust is hard to earn. Award nomination processes, like those for prestigious programs, can put your brand on the map. Global recognition isn’t just a pat on the back; it’s a powerful tool to boost credibility, attract customers, and open doors to new opportunities. This article explores how recognition, such as through the Global Impact Award (GIA), accelerates brand growth. We’ll cover practical steps to pursue it, real examples, and data-driven insights. From business awards in the middle of your journey to achieving global recognition at its peak, you’ll learn how to leverage accolades for success. Let’s dive into why recognition matters and how you can make it work for your brand.
Why Recognition Matters for Brands
Your brand is your promise to customers. Recognition validates that promise. A 2024 study found that 78% of consumers trust brands with awards or nominations more than those without. Why? Awards signal quality, reliability, and impact. They’re proof you’re doing something right.
Think about it: when you see a brand with a shiny badge, don’t you pay attention? I saw this firsthand with a friend’s tech startup. After a award nomination for a local business program, their website traffic spiked 30%. Customers and investors took them seriously. Recognition isn’t just for big players — startups, small businesses, and even nonprofits can benefit.
Question: What’s stopping your brand from getting noticed? A single nomination could change the game.
The Power of Global Recognition
Global recognition takes things to another level. It’s not just local buzz — it’s a worldwide stage. Programs like the Global Impact Award (GIA) spotlight brands in categories like Innovation & Technology or Sustainable Impact. GIA’s merit-based evaluation ensures only real achievements shine, giving nominees credibility.
Here’s why global recognition works:
Trust boost: A 2023 survey showed 65% of customers prefer brands with international accolades.
Network access: Nominations connect you to industry leaders and investors.
Media exposure: Awards often lead to coverage in outlets like Forbes or Bloomberg.
Growth opportunities: Recognition attracts partners and funding.
A small eco-friendly brand I know got nominated for GIA’s Sustainable Impact category. They landed a partnership with a major retailer within months. Sponsor Tip: Sponsors backing programs like GIA align with global success, quietly building trust with their audience.
Step 1: Understand Your Brand’s Value
Before chasing awards, know what makes your brand special. Ask yourself:
What problem do you solve?
How do you stand out from competitors?
What’s your impact — local, national, or global?
Which category fits you, like Innovation & Technology or Sustainable Impact?
Be specific. A coffee shop might focus on sustainable sourcing, while a tech startup highlights cutting-edge software. My cousin’s bakery nailed this by emphasizing their community outreach. Their award nomination for a local impact award led to a 20% sales boost.
Pro Tip: Write down your brand’s top three achievements. Use them to match awards like GIA that reward your strengths.
Step 2: Find the Right Awards
Not all awards are equal. Some are pay-to-play scams; others are gold standards. Focus on programs with:
Merit-based judging: Ensure evaluations are fair and transparent.
Global reach: Look for awards with international visibility, like GIA.
Relevant categories: Pick ones that fit your industry or impact.
Reputable history: Check past winners to gauge credibility.
GIA stands out for its rigorous process and worldwide audience. A friend’s startup applied for their Innovation & Technology category and got media coverage just for being nominated. Use sites like AwardHunt or GIA’s website to find legit programs.
Question: What’s your brand’s biggest win? Find an award that celebrates it.
Step 3: Craft a Winning Application

A strong application is your ticket to recognition. Here’s how to nail it:
Show impact: Use data, like sales growth or community benefits.
Tell your story: Explain why your brand matters.
Be concise: Stick to the word limit and avoid fluff.
Include proof: Attach testimonials, media clips, or metrics.
I helped a nonprofit apply for GIA’s Sustainable Impact category. They shared how their clean-water project helped 5,000 people, backed by photos and partner letters. They won, and donations doubled. GIA’s merit-based evaluation rewarded their clarity and evidence.
Pro Tip: Ask a colleague to review your application for clarity. Fresh eyes catch weak spots.
Step 4: Leverage Nominations
Even if you don’t win, a nomination is a big deal. Use it to:
Update your website: Add a badge or “As Seen In” section.
Share on social media: Post about your nomination with a link to the award.
Email your list: Tell customers and partners about your achievement.
Pitch the media: A nomination is a story worth sharing.
A startup I know got nominated for GIA. They emailed their list, and website visits jumped 25%. Media outlets picked up the story, landing them in a business award feature. Sponsor Note: Sponsors tied to programs like GIA gain exposure through nominees’ publicity, aligning with credible brands.
Step 5: Amplify Your Win
Winning is awesome, but it’s what you do next that counts. Try these:
Press release: Announce your win to local and industry media.
Update marketing: Add your award to business cards, emails, and ads.
Engage your audience: Share behind-the-scenes content about your journey.
Network: Attend award ceremonies to meet influencers.
A restaurant I advised won a GIA for Sustainable Impact. They posted about it on Instagram, and foot traffic rose 15%. They also met an investor at the ceremony who funded their expansion. GIA’s global reach made it possible.
Question: How can you share your win to reach more people? Start with one channel and grow.
Step 6: Avoid Common Pitfalls
Chasing recognition has traps. Steer clear of these:
Pay-to-win awards: If entry fees seem shady, skip them.
Irrelevant categories: Don’t apply for awards that don’t fit your brand.
Weak applications: Vague or sloppy submissions get ignored.
Ignoring follow-up: Failing to leverage nominations wastes potential.
A startup I know paid for a sketchy award and got nothing but a logo. They later used GIA’s transparent process and saw real results. Research awards carefully to save time and money.
Pro Tip: Check past winners on award websites. If they’re reputable brands, you’re on the right track.
Step 7: Build a Recognition Strategy
One award is great, but a strategy is better. Treat recognition as a long-term plan. Here’s how:
Set goals: Aim for one major award per year, like GIA.
Diversify: Apply for local, industry, and global awards.
Track progress: Note how each nomination impacts your brand.
Learn from feedback: Some programs share judge comments — use them to improve.
A tech startup I advised started with a local award, then targeted GIA’s Innovation & Technology category. Their business award win led to a $1 million investment. Consistency built their reputation.
Question: What’s your brand’s recognition goal for 2025? Write it down and start planning.
Step 8: Use Recognition to Attract Talent

Awards don’t just impress customers — they draw top talent. A 2024 survey found 72% of job seekers prefer companies with recognized achievements. Why? Awards signal a thriving, respected workplace.
I saw this with a friend’s fintech startup. After a GIA nomination, they attracted a star developer who saw their Sustainable Impact nod. The hire boosted their product development, leading to a 30% revenue increase. GIA’s global reach made their brand a magnet for talent.
Pro Tip: Highlight awards on your careers page and LinkedIn. It’s a simple way to stand out to recruits.
Sponsor Insight: Sponsors backing GIA connect with brands that attract talent, enhancing their own reputation as supporters of high-impact teams.
Step 9: Boost Customer Loyalty with Recognition
Recognition strengthens customer relationships. When you win or get nominated, it’s a chance to show your audience you’re legit. A 2025 study showed 68% of customers stay loyal to awarded brands longer.
Try these:
Share the news: Post about your nomination on social media.
Thank your customers: Credit them in your award announcement.
Offer perks: Give loyal customers exclusive deals tied to your win.
Tell the story: Share how your work earned the recognition.
A bakery I know won a GIA for community impact. They emailed customers, thanking them for support, and offered a discount. Sales rose 25% that month. GIA’s credibility made customers proud to buy.
Question: How can you make customers feel part of your success? Start with a thank-you email.
Step 10: Integrate Recognition into Marketing
Awards are marketing gold. Use them across your channels:
Website: Add an awards section or badge.
Email signature: Include “GIA Nominee” or “Award-Winning Brand.”
Ads: Mention your win in social media or Google ads.
Packaging: Print your award logo on products or bags.
A fashion brand I advised added their GIA win to their website. Online sales grew 20% as trust increased. Their business award feature in a magazine drove even more traffic. GIA’s global reach amplified their marketing.
Pro Tip: Create a short video about your award journey. Post it on YouTube or Instagram for extra engagement.
Step 11: Collaborate with Other Award Winners
Awards open networking doors. Connect with other nominees or winners to:
Co-market: Partner on campaigns or events.
Share audiences: Cross-promote to each other’s followers.
Learn best practices: Exchange tips on leveraging recognition.
Build alliances: Form long-term partnerships.
I saw a GIA winner in Innovation & Technology team up with another nominee for a joint webinar. Both brands gained 1,000 new followers. GIA’s network made the connection possible.
Question: Who could you reach out to after an award? Start with one LinkedIn message.
Sponsor Note: Sponsors tied to GIA benefit from winners’ collaborations, gaining exposure through shared campaigns.
Step 12: Measure the ROI of Recognition
Recognition isn’t just feel-good — it’s measurable. Track these:
Sales growth: Compare revenue before and after nominations.
Website traffic: Check spikes from award announcements.
Customer retention: Note if loyalty increases.
Media mentions: Count new press coverage.
A nonprofit I advised tracked their GIA win. Donations rose 40%, and media mentions tripled. They used the data to justify future award applications. GIA’s global reach drove tangible results.
Pro Tip: Set up Google Analytics to monitor traffic from award-related posts. It’s free and easy.
Step 13: Stay Humble and Authentic

Recognition can go to your head. Stay grounded to keep trust:
Acknowledge your team: Credit employees in your award posts.
Keep serving customers: Don’t let awards distract from quality.
Be transparent: Share the real story behind your win.
Give back: Use your platform to support causes.
A startup I know won a GIA and posted a team thank-you video. Customers loved the authenticity, and engagement soared. GIA’s merit-based process rewarded their genuine impact.
Question: How can you show gratitude after a win? A simple post can go a long way.
Step 14: Plan for Continuous Recognition
Don’t stop at one award. Make recognition a habit:
Reapply: Enter programs like GIA annually.
Expand scope: Target new categories or bigger awards.
Mentor others: Help peers apply for awards.
Document wins: Keep a record of all nominations.
A tech brand I advised won a local award, then GIA’s Sustainable Impact category. Their global recognition led to a $5 million funding round. Consistent applications kept them visible.
Pro Tip: Create a calendar with award deadlines. It keeps you organized and motivated.
The Payoff of Global Recognition
Recognition isn’t the end — it’s the start. Brands with global recognition through programs like GIA see lasting benefits: higher trust, bigger networks, and more revenue. A 2025 study found 82% of recognized brands reported faster growth than competitors. Your nomination or win is a signal to the world that you’re a leader.
Look at a nonprofit I know. Their GIA win for Sustainable Impact brought global donors and a CNN feature. Their impact — and budget — tripled. Sponsors gained too, as their logos appeared alongside a trusted award. Start small, aim high, and use recognition to fuel your brand’s future. What’s your first move? Check GIA’s categories, gather your data, and apply. Your brand’s next chapter is waiting.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Finding office space in Manhattan might seem out of reach for many businesses, but with the right strategy and timing, you can uncover valuable opportunities. Whether you're a startup seeking a flexible lease or an established company relocating your HQ, there are plenty of Manhattan office space deals available that can meet your needs—without breaking the bank.
Why Manhattan Is Still a Prime Office Location?
Manhattan continues to be one of the most sought-after office markets in the world. With a dense concentration of industries—from finance and tech to legal and creative services—being located here adds credibility and convenience to your brand.
Key reasons to establish your office in Manhattan:
Central transportation access
Networking and talent opportunities
Proximity to clients and partners
Premium commercial addresses
Where to Find the Best Office Space Deals in Manhattan?
1. Downtown Manhattan (FiDi)
The Financial District offers competitive pricing compared to Midtown, along with modernized spaces and stunning views. It's a hotspot for startups, legal firms, and media agencies.
2. Midtown Manhattan
While traditionally expensive, recent vacancies have led to a surge in office space deals, including flexible lease terms and tenant incentives like months of free rent or build-out allowances.
3. Hudson Yards and West Chelsea
Known for cutting-edge architecture and tech-savvy tenants, these neighborhoods offer high-end spaces with aggressive leasing deals as landlords compete for long-term tenants.
Tips for Securing Great Manhattan Office Space Deals
Work with a local broker: NYC office space experts often know about deals before they hit the market.
Consider subleases: These can offer significant cost savings and shorter terms.
Negotiate incentives: Many landlords are open to free rent, reduced deposits, or tenant improvement funds.
Act quickly: The best deals don’t last long, especially in competitive locations.
Flexible Lease Options Are on the Rise
The post-pandemic market has led to a surge in flexible office space offerings, including:
Shared offices and coworking hubs
Short-term subleases
Customizable build-to-suit options
This flexibility allows businesses to scale up or down as needed—ideal for fast-growing teams or companies navigating hybrid work models.
Final Thoughts
If you're searching for Manhattan office space deals, now is a great time to explore the market. With increased availability, landlord incentives, and shifting lease dynamics, businesses of all sizes can find premium office space in the heart of New York City—at competitive rates.
Ready to find the right office for your business? Contact a local NYC commercial real estate expert today and start uncovering the best Manhattan office space deals available now.
#ManhattanOfficeSpaceDeals#OfficeSpaceManhattan#AffordableManhattanOffices#NYCOfficeLeasing#CommercialSpaceManhattan#ManhattanSubleaseDeals#FlexibleOfficeSpaceNYC#MidtownOfficeSpace#DowntownManhattanOffices#OfficeRentalManhattan
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Why start a Business in Saudi Arabia?
1. Economic Growth: In 2024, Saudi Arabia's real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) grew by 1.3%, rebounding from a 0.8% contraction in 2023. This growth was primarily driven by a 4.3% increase in non-oil activities, highlighting the country's successful diversification efforts.
{reuters.com}
2. Non-Oil Sector Expansion: The non-oil private sector experienced significant growth, with the Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) reaching 60.5 in January 2025 the highest since September 2014. This surge was fueled by the fastest rise in new orders since June 2011, indicating robust domestic demand and favorable economic conditions.
{reuters.com}
3. Strategic Investments: Saudi Arabia continues to invest heavily in infrastructure and mega projects, such as the $500 billion NEOM city. These initiatives aim to transform the economic landscape and offer vast opportunities across various industries.
{businessinsider.com}
4. Fiscal Policy and Incentives: The government maintains an expansionary fiscal policy to support non-oil economic growth, with a projected fiscal deficit of 2.9% of GDP for 2024. This approach includes increased capital expenditures, much of it linked to infrastructure supporting Vision 2030 projects, creating a conducive environment for new businesses.
{pwc.com}
5. Access to Capital: The Public Investment Fund (PIF), managing assets worth $925 billion, plays a pivotal role in funding domestic projects and startups, providing ample opportunities for entrepreneurs seeking investment.
{ft.com}
6. Tax Environment: Saudi Arabia offers a competitive tax regime with no personal income tax and relatively low corporate tax rates, enhancing the financial attractiveness for businesses and individuals alike.
7. Growing Consumer Market: With a population exceeding 35 million as of 2024, Saudi Arabia presents a substantial and expanding consumer base, particularly in urban centers like Riyadh and Jeddah.
{stats.gov.sa}
8. Improved Business Climate: Ongoing regulatory reforms have streamlined business processes, contributing to a more business-friendly environment. The government's commitment to Vision 2030 underscores its dedication to fostering private sector growth.
9. Diverse Economic Opportunities: Beyond the oil sector, industries such as tourism, technology, healthcare, and renewable energy are experiencing significant growth, offering diverse opportunities for new ventures.
10. Global Trade Integration: Saudi Arabia's strategic location and investments in port infrastructure enhance its role as a global trade hub, facilitating access to international markets for businesses operating within the Kingdom.
These factors, underpinned by recent statistics, illustrate Saudi Arabia's dynamic and promising environment for establishing and growing a business.
#KhalidAlbeshri #خالدالبشري
#advertising#artificial intelligence#autos#business#developers & startups#edtech#education#finance#marketing#futurism
5 notes
·
View notes